Setup Guide
This guide will give you a short introduction to the functionalities of the Netmaker platform, after installing your control plane.
First Time Log In (On-Prem Only)
On first login, you will need to create an Admin user.
Create a Network
Netmaker deploys a network by default (called "netmaker") which you can use. However, if you'd like to create your own, or have multiple, click on "Create network" in your Dashboard to add a new one.

This network should have a sensible name.
More importantly, it should have a non-overlapping, private address range.
If you are running a small (less than 254 machines) network, and are unsure of which CIDR’s to use, you could consider:
10.11.12.0/24
10.20.30.0/24
10.99.98.0/24
Network Settings Description
The Network creation form has a few fields which may seem unfamiliar. Here is a brief description:
IPv4: Adds private IPv4 to all nodes in a network
IPv6: Adds private IPv6 to all nodes in a network
Default Access Control: Indicates the default ACL value for a node when it joins in respect to it’s peers (enabled or disabled).
Once your network is created, you should see the network (Wg Net here but it will be the name you chose when creating the network):

When you click on the NetId and then the Nodes button (or go direct via the left-hand menu and then Nodes) you see that the netmaker server has added itself to the network. From here, you can move on to adding additional nodes to the network.

Create a Key
Adding nodes to the network typically requires a key. Enrollment keys offer different ways to register with a server.
By default, Netmaker will create a key you can use with your network. However, you can create your own if you would like to specify certain settings.
Navigate to the Keys interface. You should see a create button in the top right corner.

After clicking that, you should be brought to a window like this.

This will give you a few different options on how you want to set up your enrollment key. you can set it up with unlimited uses, limited uses, or timebound uses. You can also setup one or multiple networks to join, or you can set it to no networks and then join a network through the UI in the devices interface. You can also create any tags you would like for that key.

If an enrollment key runs out of uses, or is expired, the key will show as invalid like in the image below.

After your enrollment key is created, you can click on that key to get the registration token.

The Enrollment Key value is the secret string that will allow your node to authenticate with the Netmaker network. This can be used with existing netclient installations where additional configurations (such as setting the server IP manually) may be required. This is not typical. E.g.
netclient register -k <enrollment key> -s grpc.myserver.com -p 50051The Registration Token value is a base64 encoded string that contains the server IP and grpc port, as well as the enrollment key. This is decoded by the netclient and can be used with existing netclient installations like this:
netclient register -t <registration token>. You should use this method for adding a network to a node that is already on a network. For instance, Node A is in the mynet network and now you are adding it to default.The Register Command value is a command that can be run on Linux systems after installing the Netclient. It will register with the server directly from the command line.
Other variations (eg Docker) are covered with the remaining values.
Deploy Nodes
Nodes act as the endpoints of your network, and can perform special networking tasks such as relaying traffic and forwarding traffic to local environments. Nodes are deployed with the Netclient.
You should get output similar to the below. The netclient retrieves local settings, submits them to the server for processing, and retrieves updated settings. Then it sets the local network configuration. For more information about this process, see the client installation documentation. If this process failed and you do not see your node in the console (see below), then reference the troubleshooting documentation.
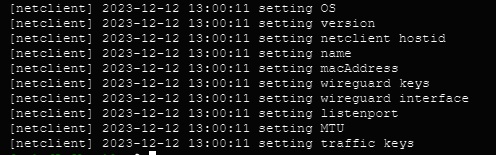
Repeat the above steps for every machine you would like to add to your network. You can re-use the same install command so long as you do not run out of uses on your access key (after which it will be invalidated and deleted).
Once installed on all nodes, you can test the connection by pinging the private address of any node from any other node.
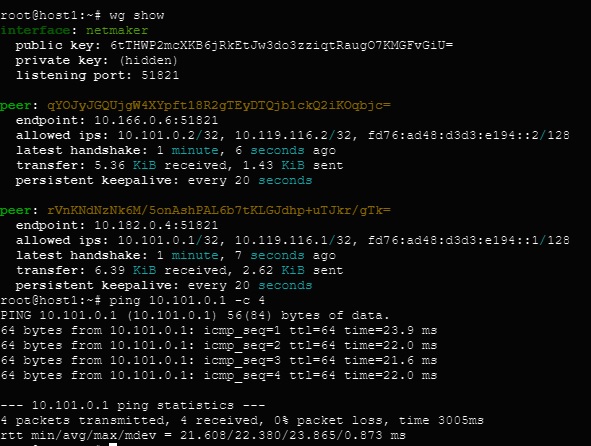
Manage Devices
Your machines should now be visible in the control panel.

Each node has an associated device. Nodes represent the device within a network, while the device remains the same across networks. The device will have settings like verbosity and listen ports which can be modified. The Device can be found in the Devices tab on the UI. You should be taken to a screen like this.

In here you can see the device's name, the endpoint of the server running netclient, the public key for that host, the version number, and a switch to set that host’s node as the default node. When this is switched on, that node will serve as the default node when a network is created. Clicking on a device will bring you to the device details.

This will give you more information like the firewall in use, MTUs, and listening port. You can also see networks associated with that device and options to edit or delete the device. If you are going to delete a device.

In the edit screen, you can make changes to the logging verbosity, listening port and proxy listening port, local range, MTU, and name. These fields will also update in the node, as the node gets this info from the device. If you want to change the endpoint, the associated node has to be static.
You can view/modify/delete any node by selecting it in the NODES tab. For instance, you can change the name to something more sensible like “workstation” or “api server”. You can also modify network settings here, such as keys or the WireGuard port. These settings will be picked up by the node on its next check-in. For more information, see Advanced Configuration in the Using Netmaker docs.

Nodes can be added/removed/modified on the network at any time. Nodes can also be added to multiple Netmaker networks. Any changes will get picked up by any nodes on a given network and will take about ~30 seconds to take effect.
Uninstalling the netclient
Uninstalling Netmaker
To uninstall Netmaker from the server, simply run:
Or to remove the docker volumes for a future installation:
Last updated
Was this helpful?